Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a buzzword across nearly every industry. From healthcare to finance, logistics to social media, AI is seen as the driver of innovation. Automated Traffic Enforcement (ATE) is no exception. Yet amid the excitement, one critical misunderstanding often emerges: the difference between Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
At Elovate, we believe in clarity and transparency, not only in how enforcement programs operate, but also in the technologies that make them possible. With this blog, we aim to demystify AI vs. ML, explain where each fits in ATE, and address common concerns around privacy and human oversight.
Machine Learning vs. Artificial Intelligence
While often used interchangeably, AI and ML are not the same.
- Machine Learning (ML) has been around for decades. It refers to systems that learn patterns from large datasets and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. Think of it as training a model: feed it thousands of examples, and it learns to recognize patterns more efficiently over time.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a subset of ML. It focuses on creating systems that can mimic aspects of human intelligence, such as decision-making, problem-solving, or perception. In practice, AI leverages ML but applies it in more specialized and often more complex contexts.
For ATE, this distinction matters. ML has long been the foundation of functions like license plate recognition (ALPR) or speed tracking. AI builds on this, introducing tools that can streamline image review, filter false positives, and improve system reliability — all without removing humans from the process.
From Science to Streets: AI’s Broader Journey
To understand why AI is now part of ATE, it helps to look at its trajectory more broadly. In science, AI for example powers medical imaging – helping radiologists spot early signs of disease. In retail, it enables personalized recommendations. In finance, it detects fraud in real time.
These are all environments where accuracy, trust, and accountability are paramount. The same principles apply to traffic safety. AI is not at all about removing humans, it is about supporting them with tools that are faster, more reliable, and less prone to error caused by fatigue or oversight.
Addressing the Skepticism
Public and governmental skepticism around AI is natural. New technologies often raise questions:
- Will this replace human judgment?
- Are there new privacy risks?
- Can machines really be trusted to make fair decisions?
The short answer: AI in ATE complements, rather than replaces, human review. At Elovate, AI is used to process events more efficiently, filter out non-violations, and prepare clean data for human reviewers. But the decision to issue a citation always involves human oversight.
On the topic of privacy: AI does not create additional risks. The way data is captured and processed follows the same stringent safeguards already in place. License plates, images, and event data are handled securely, and irrelevant or rejected data is stored or deleted according to policy.
How It Works: AI, Human, and Hybrid Review
The graphic below illustrates how AI and human review intersect across the ATE process.
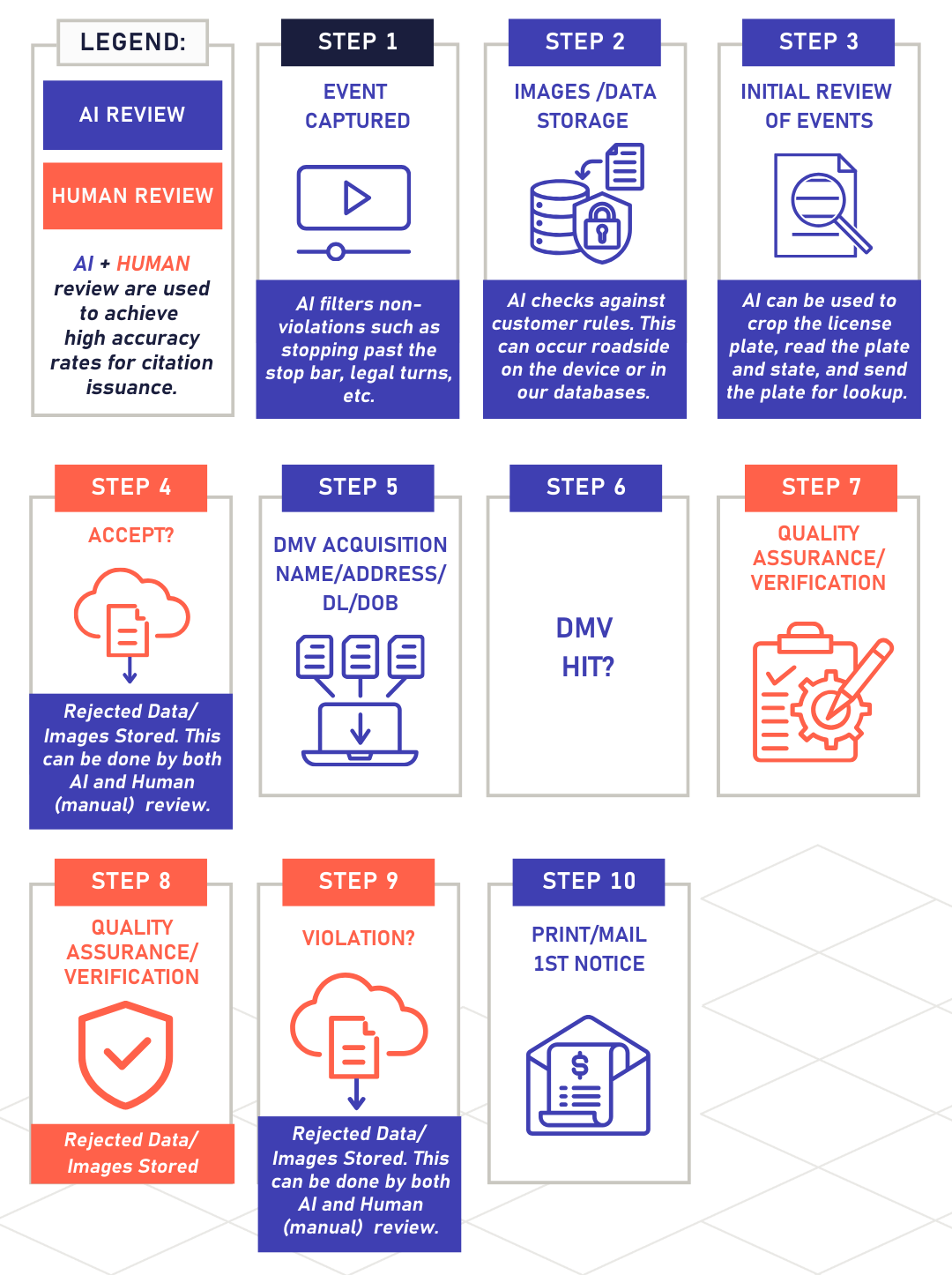
Here’s a simplified walkthrough:
- Event Captured – A violation event is triggered, and AI checks it against program rules.
- Initial Review – AI performs tasks like cropping the license plate, reading the characters, and preparing the record.
- Image/Data Storage – Data is securely stored.
- Filtering – AI can filter out non-violations (e.g., legal right turns, stopping past the stop bar).
- DMV Lookup – AI submits plate details for DMV acquisition.
- Human Oversight – At multiple checkpoints, humans review the AI-processed events. They verify accuracy, ensure context, and reject non-violations.
- Quality Assurance – A hybrid of AI + human review ensures extremely high accuracy before citation issuance.
- Citation Issuance – Only after quality checks are complete does a citation get printed and mailed.
This hybrid system ensures efficiency without sacrificing fairness. AI reduces the workload, speeds up processes, and minimizes false positives, but humans remain central to every enforcement decision.
Why This Matters for Communities
By clarifying AI’s role, we hope to address misconceptions that may stall adoption of life-saving enforcement programs. Communities should know that:
- Safety is the goal. AI is used to make programs more effective, not to increase citations.
- Humans remain in control. Every step involving judgment includes human verification.
- Privacy remains protected. No additional personal data is collected or exposed through AI use.
The result is stronger compliance, safer roads, and greater trust between municipalities and the public.
The Road Ahead with AI in Enforcement
AI and ML are powerful tools, but they are not magic, and they are not replacements for human oversight. ML has long powered core functions of ATE, while AI is a natural next step that improves speed, accuracy, and reliability. By combining the strengths of both with rigorous human review, Elovate delivers enforcement solutions that are transparent, equitable, and effective.
As AI continues to shape industries everywhere, its role in traffic enforcement will grow, but always with the same guiding principle: supporting human judgment to build safer, fairer communities.






