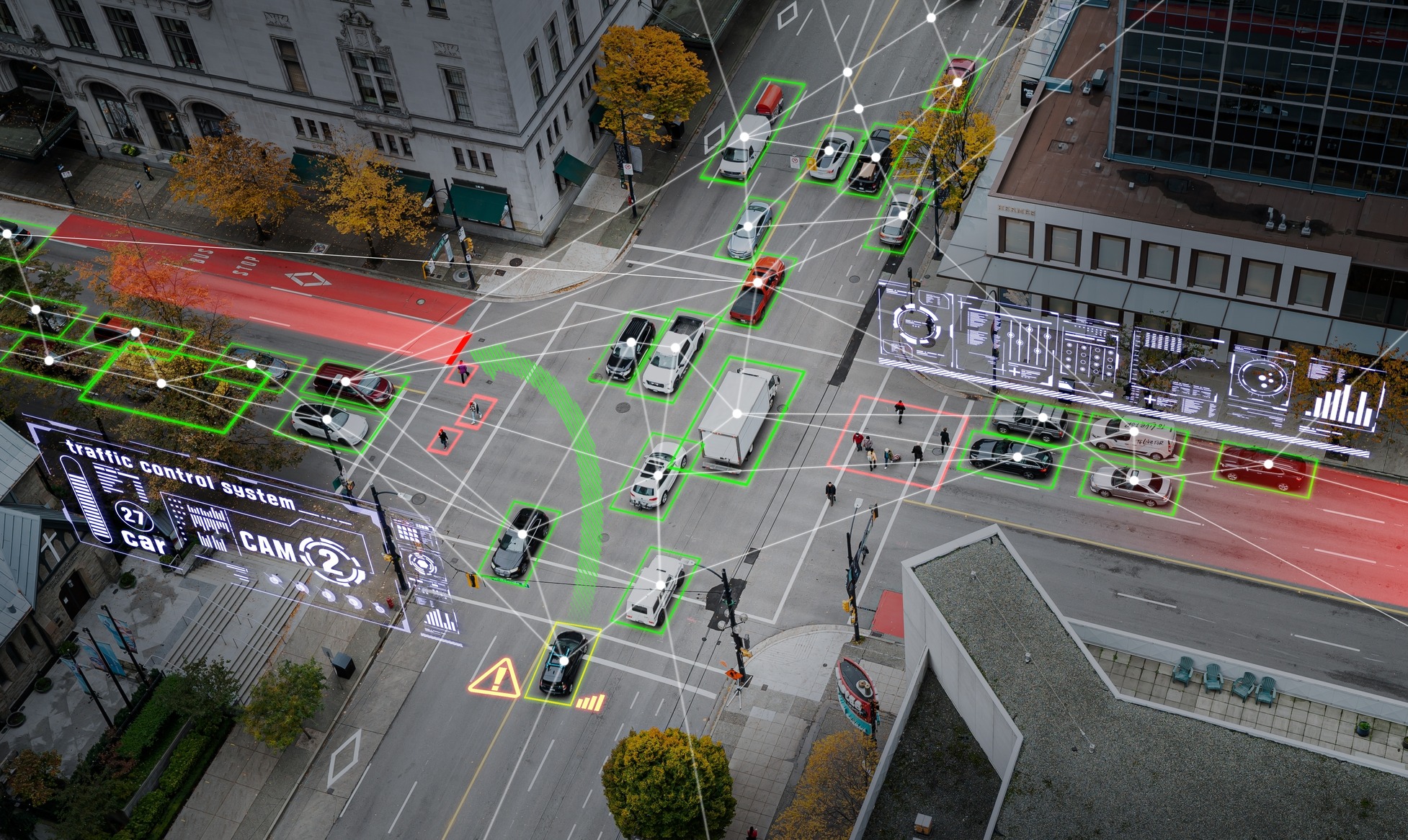
As the world increasingly embraces smart city initiatives, automated speed enforcement technologies are becoming critical tools for improving road safety. These systems are evolving rapidly, powered by innovations in artificial intelligence (AI), scanning LiDAR technology, and big data analytics. Coupled with progressive legislation, these advancements promise to revolutionize traffic enforcement and encourage broader adoption across the United States and all around the globe. In this blog, we explore the latest trends in automated speed enforcement and the outlook for these intelligent, fully integrated solutions in 2025.
Technological Innovations Driving Automated Speed Enforcement
1. AI-Powered Enforcement Cameras
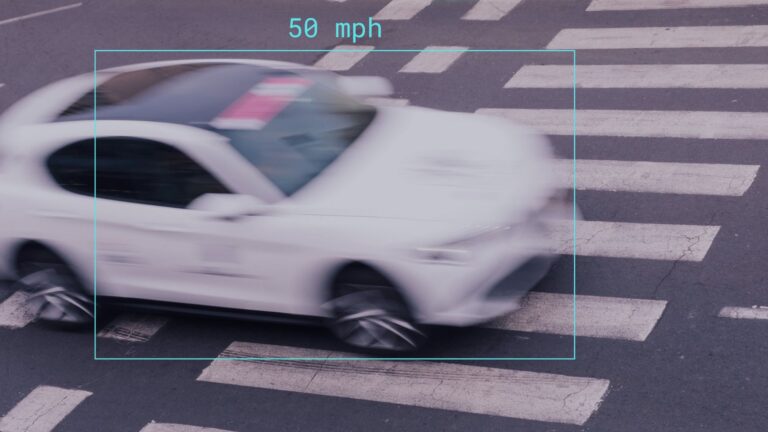
One of the most significant technological trends is the integration of machine learning and, in particular, artificial intelligence into speed enforcement cameras. AI-driven systems enhance the accuracy of detecting violations, including speeding, illegal mobile phone use, and even seatbelt non-compliance. For example, AI-enabled cameras in Western Australia are set to go live in early 2025, targeting drivers using phones or failing to wear seatbelts while also monitoring speed violations. These systems can process vast amounts of data in real-time, reducing false positives and increasing efficiency.
2. Advanced Radar and Super-Resolution Imaging
In the UK, new enforcement cameras featuring 4D radar and super-resolution imaging* are currently under trial. These technologies allow for simultaneous monitoring of multiple lanes and can detect a range of violations, from speeding to driving without insurance and even monitor the behavior of speeding drivers inside the vehicle.
3. Integration with Big Data and Predictive Analytics
Automated enforcement systems are increasingly being integrated with big data platforms. These platforms enable predictive analytics, helping cities identify high-risk areas, and deploy resources more effectively. For instance, traffic data collected from enforcement cameras can be analyzed to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and prevent accidents. Such integrations align with broader smart city objectives, creating safer and more efficient urban environments, and often consider social equity issues in regard to camera placement.
4. Impact of Connected Driving and Autonomous Vehicles
Connected driving and autonomous vehicles are starting to reshape the landscape of automated traffic enforcement. Vehicles equipped with vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication can exchange real-time data with enforcement systems, enabling more dynamic monitoring and immediate feedback to drivers. Additionally, autonomous vehicles – designed to adhere strictly to traffic laws – are expected to reduce violations like speeding and reckless driving, presenting both opportunities and challenges for traffic enforcement agencies. These technologies may require enforcement systems to adapt, focusing less on individual violations and more on system-level safety and compliance monitoring.
Adoption Trends in the United States
The U.S. currently presents a patchwork adoption of automated speed enforcement, with legislation and implementation varying by state. However, the momentum is building as more states recognize the benefits of these systems.
- Maryland: A leader in automated enforcement, Maryland has long used speed cameras in school and construction zones to improve safety. Recent upgrades and expansions to its systems include the integration of machine learning and expanded deployment to reduce speeding fatalities further.
- Florida: Florida is exploring pilot programs for automated speed enforcement in urban areas with high pedestrian traffic. These programs aim to address the state’s rising rates of road accidents and traffic violations.
- Pennsylvania: Automated speed enforcement is gaining traction in Pennsylvania, particularly in work zones, where new legislation supports its deployment to protect workers and reduce accidents.
- Chicago: Chicago remains at the forefront of automated traffic enforcement in the U.S., with extensive use of red-light and speed cameras. The city’s focus on expanding coverage to underserved neighborhoods ensures equity in enforcement while improving road safety.
- Washington State: Washington will be launching a state-wide work zone enforcement program early in 2025 leveraging state-of-the-art technologies such as advanced scanning LiDAR, real-time speed monitoring, and automated citation processing,
Global Adoption Trends
Automated speed enforcement is becoming a global trend as countries seek to reduce traffic fatalities and improve compliance with traffic laws.
- Cyprus: The government of Cyprus has been implementing enhanced speed enforcement systems since early 2022 and is currently expanding its programs. These efforts are part of a broader initiative to modernize the country’s traffic enforcement infrastructure, and Cyprus now leads the European countries in the decrease of road deaths since starting Automated Speed Enforcement
- European Union: Many EU countries are scaling up their use of automated enforcement as part of Vision Zero initiatives, aiming to eliminate all traffic fatalities and severe injuries. Advanced systems in Sweden, the birthplace of the vision zero initiative, and the Netherlands, with its integrated AI and radar technologies, are currently setting benchmarks for effectiveness and public acceptance.
- Australia: Western Australia’s deployment of AI cameras represents a significant leap forward. The system’s ability to detect multiple violations simultaneously is expected to influence other countries considering similar technologies.
- India: With its high rate of road fatalities, India is also investing in automated enforcement systems and AI-based ITMS (Intelligent Traffic Management Systems)**. Pilot programs in major cities are testing the scalability and effectiveness of these technologies.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
2025 brings both new opportunities and challenges for automated traffic enforcement (ATE). With the rise of connected driving and autonomous vehicles, ATE systems have the potential to integrate seamlessly with advanced vehicle technologies, enabling dynamic enforcement and proactive safety measures. However, these advancements also pose challenges, such as adapting systems to monitor compliance in a largely autonomous driving environment and addressing the ethical considerations of constant data exchange.
Despite the clear benefits, automated speed enforcement will continue to face certain challenges. Privacy concerns, the potential for over-enforcement, and the cost of deployment are key barriers to widespread adoption. Public education and transparent implementation will be critical to addressing these issues.
Looking ahead, ATE technologies can play a pivotal role in enhancing urban planning by providing critical traffic flow data, identifying high-risk intersections, and informing infrastructure investments. Additionally, ATE systems can provide valuable data to promote social equity by ensuring fair and equal camera placement and enforcement as well as reducing accident rates in historically neglected areas. By leveraging these innovations, cities and states can create safer, more equitable, and efficiently managed transportation networks.
*New AI Speed Cameras: A Revolutionary Step for UK Road Safety – Highways Industry
**The Tech Behind Your Traffic Challan: How AI tracks your every move on the road